What Three Parts Make Up the Nervous System Try Again
The nervous system: Facts, office & diseases
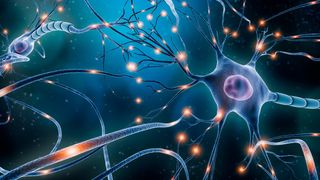
The nervous organisation is a complex drove of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals betwixt different parts of the torso. It is essentially the body'due south electrical wiring.
Structurally, the nervous arrangement has ii components: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous arrangement. According to the National Institutes of Health, the fundamental nervous system is made upwardly of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. The peripheral nervous organisation consists of sensory neurons, ganglia (clusters of neurons) and nerves that connect to 1 another and to the central nervous arrangement.
Functionally, the nervous system has two main subdivisions: the somatic, or voluntary, component; and the autonomic, or involuntary, component. The autonomic nervous system regulates certain torso processes, such as blood force per unit area and the rate of breathing, that work without conscious effort, co-ordinate to Merck Manuals. The somatic system consists of fretfulness that connect the brain and spinal cord with muscles and sensory receptors in the skin.
Description of the nervous organization
Nerves are cylindrical bundles of fibers that get-go at the brain and central cord and co-operative out to every other part of the body, according to the University of Michigan Medical School.
Neurons send signals to other cells through thin fibers called axons, which crusade chemicals known every bit neurotransmitters to be released at junctions called synapses, the NIH noted. At that place are over 100 trillion neural connections in the average homo brain, though the number and location tin vary. For example, a study published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) institute that out of the 160 participants studied, the brains of highly artistic people have more connections amid 3 specific regions of the brain than less creative thinkers.
"You have these three different systems that are all located in different parts of the brain, but they are all co-activated at once," said lead study author Roger Beaty, a postdoctoral fellow studying cognitive neuroscience at Harvard University. "People who are better able to co-activate them [came] upward with more-creative responses."
A synapse gives a command to the cell and the unabridged communication procedure typically takes only a fraction of a millisecond. Signals travel forth an alpha motor neuron in the spinal cord 268 mph (431 km/h); the fastest manual in the homo body, according to Discover magazine.
Sensory neurons react to physical stimuli such as light, sound and bear on and ship feedback to the key nervous system about the body's surrounding environs, according to the American Psychological Clan.
Motor neurons, located in the central nervous organization or in peripheral ganglia, transmit signals to activate the muscles or glands. Glial cells, derived from the Greek word for "glue," are specialized cells that support, protect or nourish nerve cells, co-ordinate to the Oregon Institute of Wellness and Science Academy.
The brain's connections and thinking ability grew over thousands of years of development. For example, a virus jump its genetic lawmaking to the genome of four-limbed animals, and the code tin still be institute in humans' brains today, according to two papers published in the Jan 2018 journal Prison cell. This code packages up genetic information and sends it from nerve cells to other nearby nervus cells, a very important process in the brain.
Divisions of the nervous system
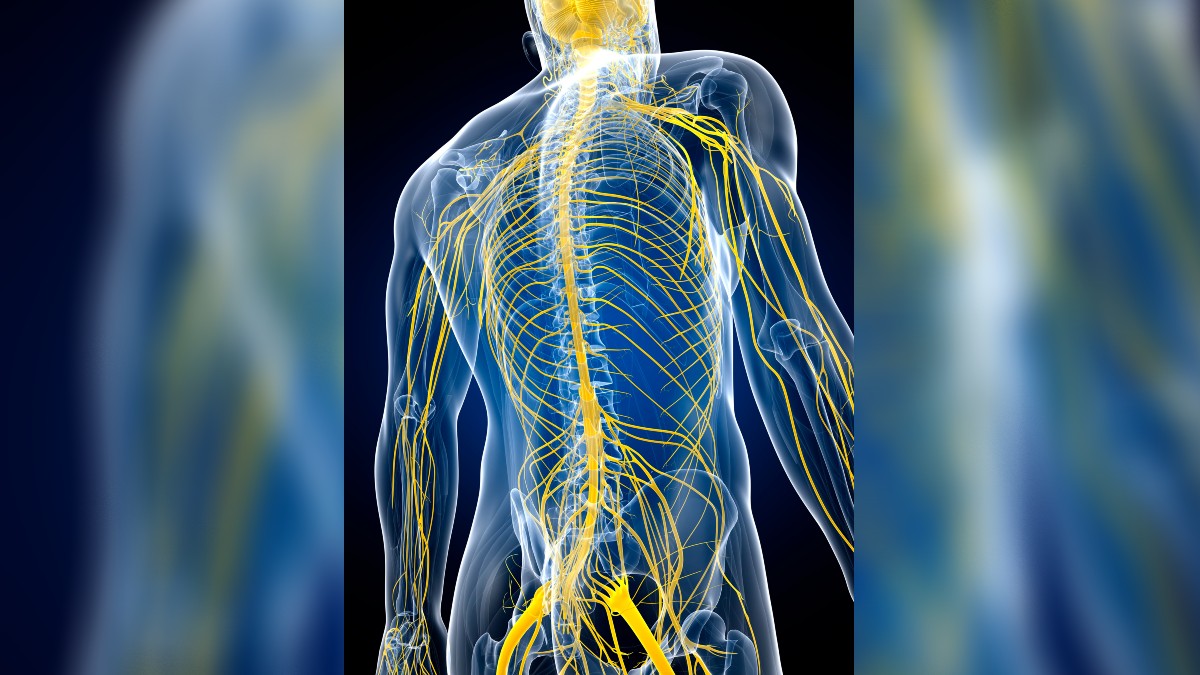
When nosotros remember of the nervous system, our thoughts immediately go to the brain. The encephalon is a hive of neuronal activity, with billions of interwoven neurons firing to preserve and recall memories, coordinate thoughts and spoken communication, and plan hereafter actions. Along with the spinal cord, the bone-clad parts of our nervous organisation are naturally called the central nervous system.
The majority of our neurons are shielded backside protective fluid and bone, where they receive signals from and dictate to organs around the body. Withal, the signals sent from the central nervous organisation must have some means of reaching their target organs. And for that they need to connect to fretfulness that stretch from the central nervous arrangement all the fashion to the extremities of the trunk. This second network of nerves is called the peripheral nervous system. Together, the central and peripheral form the major divisions of the nervous arrangement, according to the National Cancer Establish.
The peripheral nervous organisation is responsible for many functions, and equally such has numerous sub-divisions that specialise on different tasks. The sensory, or afferent, division receives signals from the periphery and carries these into the cardinal nervous organization. The motor, or efferent, division transmits signals for actions outward from the primal nervous organisation to the peripheral organs and muscles. These motor functions come in 2 forms: somatic, and autonomic. Somatic functions are perhaps the easiest concept of the nervous system to grasp, as these dictate all our voluntary actions, such as choosing to pick up a cup, or jump on the bed, co-ordinate to the medical library LibreTexts.
Not all somatic motor functions are voluntary, nevertheless. Some are automatic, pre-programmed responses built into our bodies that help us cope with danger, known every bit somatic reflexes. You lot'll notice such a reflex when you accidentally touch a hot stove, step on a sharp object, or something flies toward your eye - your trunk reacts before y'all're aware of it. Your hand pulls away, you hop onto the other pes, your eyelid slams shut. This is all the piece of work of somatic reflexes, which tin act incredibly apace as they practice non require voluntary input from the brain. Such reflexes can come in different flavours; pulling your hand away from danger is known every bit a flexor or withdrawal reflex, whereas stepping on a sharp object initiates a crossed-extensor reflex. This latter reflex automatically triggers multiple motor functions, every bit one leg retracts the other leg simultaneously expands and becomes more stable, preventing us from falling over.
The innate, hard-wired reflex responses of our peripheral nervous organization help keep us rubber from danger, simply they are not the but automatic functions performed by the peripheral nervous organization. When actions are not voluntary, or somatic, they are autonomic, which means they operate independently of conscious idea. Such processes include the heart trounce, the churning of food in the digestive tract by contracting muscles, and respiration. While our brain tin assume command of a few of these processes (remember of holding your jiff), autonomic functions will continue to operate even when we fall asleep or if we are knocked unconscious.
The processes that we cannot command, however, are by no means unchanging. Instead the organs under the control of the autonomic nervous system are regulated by a residue between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Depending on the stimulus, these systems increase or decrease activity of our internal organs, helping to ensure our body is always ready to respond to the challenge at paw.
Diseases of the nervous arrangement
"Of all the diseases of the nervous system, the almost common difficulty that people have is pain, and much of that is nervus-related," according to Dr. Shai Gozani, founder and CEO of NeuroMetrix, a medical device company. "There are 100 million people who live with chronic pain."
Parkinson's affliction
The basal ganglia are found deep within the brain, in an area responsible for controlling movement. These nerves produce a compound known as dopamine, which is important in coordinating numerous functions including executive functions and motor control. Although the cause is not withal clear, sometimes the basal ganglia can become impaired and brainstorm to die. The result of this is Parkinson'south disease, equally the loss of dopamine gradually hampers key functions such as walking, talking, and memory recall. These effects are compounded by the loss of fretfulness responsible for producing norepinephrine, a key chemical compound in the sympathetic nervous organization needed to regulate middle charge per unit and blood pressure. Medicines that increase the corporeality of dopamine in the brain can assist combat symptoms of the disease, according to the National Institute of Crumbling.
Bell's Palsy
Major fretfulness spread outward from the key nervous system to various organs and tissues, with each powering specific functions. Cranial nerve VII is known as the facial nerve, as information technology controls many of the muscles on our face including blinking and smiling. When this nerve is inflamed, damaged, or otherwise disrupted Bell'south palsy can occur, which involves the facial muscles becoming weakened or paralysed, according to the National Establish of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. This typically affects only one side of the confront, causing symptoms such as drooping of the oral fissure on 1 side and a loss of command of an eyelid, giving the affected side a slack appearance. The full symptoms of Bell's palsy are often temporary, with some or total recovery of the affected areas occurring with six months. While it is not always articulate what causes the cranial nerve to neat and Bell's palsy to occur, scientists believe that a recurring viral infection of the nervous arrangement elicits an immune response that triggers the nerve damage.
Multiple sclerosis
Neurons are the agents of signalling in our bodies, only they do not work alone. Axons, which deport signals abroad from the neuron's jail cell trunk, are coated in a sheaf of myelin. Myelin sheaves are produced in the fundamental nervous organisation by cells chosen oligodendrocytes, enabling myelin'southward function of protecting and facilitating nerve conductivity, according to the National Multiple Sclerosis Society. In multiple sclerosis, an abnormal allowed response inside the central nervous system strips away the protective myelin and causes lots of nervus scarring (sclerosis), which gives the illness its name. Research efforts are underway to treat the disease by encouraging myelin regeneration.
Peripheral neuropathy
While several degenerative nervous organisation disorders primarily or exclusively impact the central nervous system, there are a collection of diseases that instead impact the peripheral nervous system. Together these diseases are referred to as peripheral neuropathies. As the impacted region is the peripheral nervous organisation, such neuropathies lead to loss of awareness and regulatory control of extremities. These include a loss of coordination and feeling in fingers and toes, and a lack of balance, co-ordinate to the University of Michigan Wellness. The causes of peripheral neuropathy are yet to exist fully elucidated, but scientists have determined diabetes, which causes protracted periods of high blood carbohydrate, as ane of the principal causes.
Diagnosing nervous organization conditions
In that location are a number of tests and procedures to diagnose conditions involving the nervous system. In addition to the traditional X-ray, a specialized 10-ray called a fluoroscopy examines the torso in move, such as blood flowing through arteries, co-ordinate to the NIH.
Other standard neurological exams include an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), CT scan, and an electroencephalogram (EEG), which records the brain's continuous electric activity. Positron emission tomography (PET) is a procedure that measures cell or tissue metabolism and brain activity to detect tumors or diseased tissue or tumors, the NIH noted.
A spinal tap places a needle into the spinal canal to drain a small amount of cerebral spinal fluid that is tested for infection or other abnormalities, co-ordinate to the NIH.
Study of the nervous organization
The branch of medicine that studies and treats the nervous system is called neurology, and doctors who practice in this field of medicine are called neurologists. Once they have completed medical training, neurologists complete boosted grooming for their specialty and are certified by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN).
There are as well physiatrists, who are physicians who work to rehabilitate patients who have experienced illness or injury to their nervous systems that touch their power to role, according to the ABPN.
Neurosurgeons perform surgeries involving the nervous organization and are certified by the American Association of Neurological Surgeons.
Boosted resources
For more information nearly your body'southward nervous organisation, check out "The Human Nervous Organisation" past Juergen K. Mai and "The Big Book Of The Homo Body" by Katherine Marsh
Bibliography
- James Ashley, et al, "Retrovirus-like Gag Protein Arc1 Binds RNA and Traffics across Synaptic Boutons", Cell, Volume 172, January 2018.
- Roger E. Beaty, "Robust prediction of individual artistic power from encephalon functional connectivity", PNAS, Book 115, Jan 2018.
- Valerie Ross, "Numbers: The Nervous System, From 268-MPH Signals to Trillions of Synapses", Discover Magazine, mAY 2011.
- University of Michigan Health, "Peripheral Neuropathy", August 2020.
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, " Bong's Palsy Fact Canvass", November 2021.
- National Establish of Aging, "Parkinson's Disease", May 2017.
- National Library of medicine, "Neurologic Diseases", March 2022.
- National Multiple Sclerosis Society, "What is Myelin", accessed March 2022.
Source: https://www.livescience.com/22665-nervous-system.html
0 Response to "What Three Parts Make Up the Nervous System Try Again"
Enregistrer un commentaire